Maintaining healthy blood sugar has become one of the most important wellness priorities today. With modern diets, busy lifestyles, stress, and lack of sleep, many people experience daily fluctuations without even realizing it. Whether you’re trying to support healthy energy, control cravings, or maintain stable glucose levels, understanding how blood sugar works is the first step.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know about blood sugar—what it is, how it’s regulated, signs of imbalance, and the best ways to support it naturally through food, habits, and targeted supplements.
What Is Blood Sugar?

Blood sugar, also called blood glucose, is the primary form of sugar found in your bloodstream. It comes from the carbohydrates you eat and serves as a major source of energy for your body’s cells, organs, and brain. After you eat, your digestive system breaks down food into glucose, which then enters your bloodstream.
To keep everything running smoothly, your pancreas releases insulin, a hormone that helps move glucose from your blood into your cells for energy or storage. When this process works well, blood sugar focus stays within a healthy range. But when blood sugar rises too high or drops too low, it can lead to symptoms like fatigue, mood swings, cravings, headaches, or changes in appetite.
Maintaining stable blood sugar through balanced meals, daily movement, hydration, sleep, and healthy lifestyle habits is essential for long-term energy, metabolic wellness, and overall health.
Why Glucose Matters
Your muscles, brain, and organs rely on a steady supply of glucose to function properly. In fact, your brain alone uses about half of the body’s glucose supply daily.
Role of Insulin
When blood sugar rises after a meal, your pancreas releases insulin, a hormone that helps move glucose from the bloodstream into the cells.
When Blood Sugar Spikes or Drops
- Spikes (high blood sugar): often caused by sugary or refined foods, stress, or inactivity
- Crashes (low blood sugar): can follow a spike or occur after long periods without eating
Helping your body maintain smooth, even levels throughout the day leads to more energy, steady mood, and healthier eating patterns.
Normal Blood Sugar Levels (With Ranges)
Although ranges vary slightly by source, here are widely accepted general levels:
| Measurement | Healthy Range (Approx.) |
| Fasting (morning) | 70–99 mg/dL |
| Before meals | 70–130 mg/dL |
| 1–2 hours after meals | Under 140 mg/dL |
| Bedtime | 90–150 mg/dL |
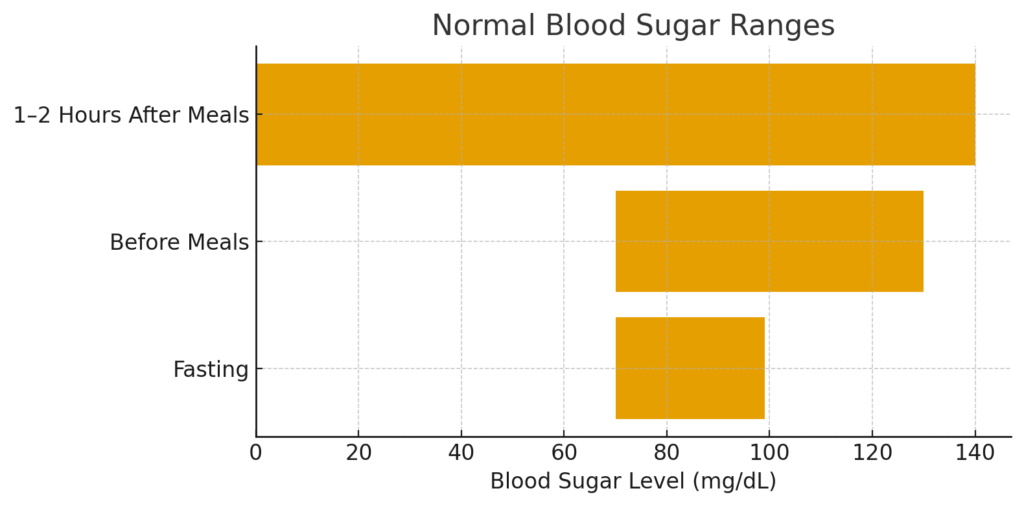
These levels shift throughout the day depending on what you eat, how much you move, and how well you sleep.
Signs of High Blood Sugar (Hyperglycemia)
High blood sugar can occur even in people without diagnosed conditions. Some common signs include:
1. Increased Thirst
When blood sugar rises, the body tries to remove excess glucose through urine. This process pulls water from your tissues, making you feel unusually thirsty. Even drinking more water might not fully satisfy your thirst if blood sugar remains high.
2. Fatigue After Meals
If blood sugar spikes quickly after eating—especially after high-carb or sugary foods—the body struggles to move glucose into the cells for energy. This leaves you feeling tired, sluggish, or sleepy shortly after meals.
3. Frequent Urination
The kidneys work hard to filter out excess sugar when levels are too high. To remove it, they produce more urine. This leads to more frequent trips to the bathroom, especially during the day or at night.
4. Blurry Vision
High blood sugar can draw fluid from the lenses of the eyes, making them swell slightly and affecting focus. This can cause temporary blurry or distorted vision until levels stabilize again.
5. Slow Energy or Difficulty Focusing
When sugar stays in the bloodstream instead of entering cells, your brain and muscles don’t get the steady fuel they need. This can result in foggy thinking, poor concentration, and sluggish mental or physical energy.
6. Headaches
Fluctuating or elevated blood sugar levels can cause dehydration, changes in blood flow, and hormonal shifts—all of which can trigger headaches. These headaches may feel dull or persistent.
7. Increased Appetite
When cells don’t receive enough energy due to poor glucose uptake, the brain thinks the body needs more fuel. This triggers hunger signals, causing increased appetite—even if you just ate.
Occasionally high blood sugar after eating is normal, but persistent symptoms should be discussed with a healthcare professional.
Signs of Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia)
Low blood sugar often appears suddenly. Watch for:
- Dizziness or shakiness
- Sweating
- Irritability
- Sudden hunger
- Weakness
- Difficulty concentrating
- Mood swings
Snacking on a quick source of carbs—like fruit juice—usually helps restore balance, but frequent episodes require professional guidance.
What Causes Blood Sugar to Rise?
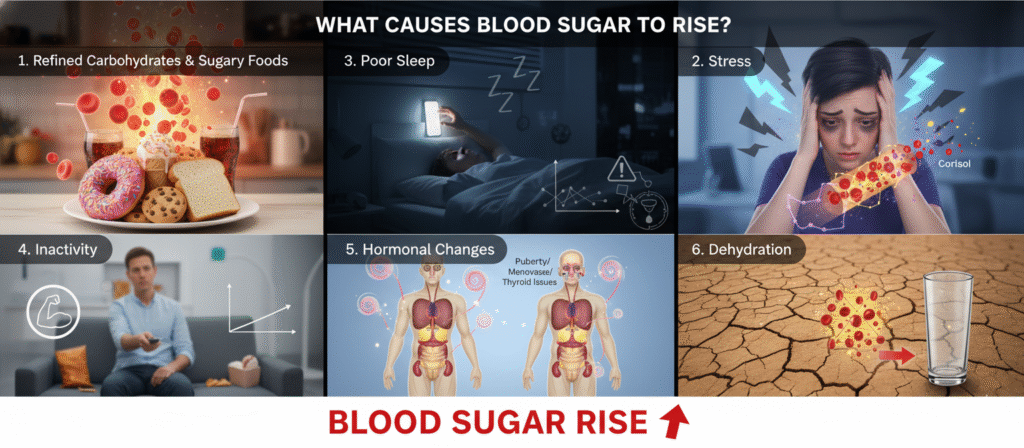
Many daily habits influence glucose levels. Common causes include:
1. Refined Carbohydrates & Sugary Foods
White bread, pastries, sodas, and sweets digest rapidly, causing quick spikes.
2. Stress
Stress triggers cortisol, a hormone that naturally raises blood sugar for “fight or flight.”
3. Poor Sleep
Just one night of poor sleep can increase insulin resistance the next day.
4. Inactivity
Movement helps absorb glucose. Sitting for long periods can lead to higher levels.
5. Hormonal Changes
Hormones such as cortisol, estrogen, and growth hormone can impact glucose balance.
6. Dehydration
Low water intake concentrates glucose in the bloodstream.
Understanding your triggers helps you build habits that naturally support balance.
How to Lower Blood Sugar Naturally
Healthy blood sugar support doesn’t require extreme diets. Here are proven lifestyle strategies:
Dietary Strategies
1. Choose Low-Glycemic Foods
Foods that digest more slowly cause gradual rises instead of sharp spikes:
- Leafy greens
- Berries
- Whole grains
- Beans
- Nuts & seeds
- Non-starchy vegetables
2. Prioritize Fiber
Fiber slows the absorption of sugar. Great sources include:
- Oats
- Chia seeds
- Lentils
- Avocado
- Vegetables
3. Balance Carbs with Protein & Fat
A meal with protein + healthy fats + complex carbs leads to steady glucose release.
4. Eat Smaller, Balanced Meals
Instead of skipping meals or overeating, aim to eat consistently throughout the day.
Lifestyle Habits
1. Walk for 10–15 Minutes After Meals
This simple habit can significantly help your body use glucose for energy.
2. Stay Hydrated
Water helps your kidneys process excess sugar.
3. Reduce Stress
Mindfulness, deep breathing, stretching, or light exercise can significantly help.
4. Improve Sleep Quality
Aim for 7–8 hours. Good sleep improves insulin sensitivity.
5. Strength Training
Building muscle improves your body’s glucose use.
Best Supplements for Blood Sugar Support

Certain nutrients and herbs may support healthy blood sugar levels when combined with lifestyle changes. These are widely researched and often included in natural formulas:
1. Cinnamon
May support healthy insulin sensitivity.
2. Berberine
A plant compound studied for metabolic support.
3. Chromium
A trace mineral involved in carb and fat metabolism.
4. Alpha-Lipoic Acid (ALA)
A powerful antioxidant that supports healthy glucose uptake.
5. Magnesium
Plays a role in hundreds of bodily functions, including glucose regulation.
6. Bitter Melon & Gymnema Sylvestre
Traditional herbs used for metabolic balance.
Note: Supplements should complement healthy habits, not replace them. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting new supplements.
Featured Section: Your Blood Sugar Support Supplement
Sugarmute – Natural Support for Balanced Blood Sugar
In today’s fast-paced world, maintaining steady blood sugar strips can be challenging. That’s why many people turn to natural supplements for additional support.
What Makes This Supplement Stand Out?
Venoplus 8 is formulated with a blend of research-backed ingredients traditionally used to support:
- Healthy glucose metabolism
- Steady energy
- Reduced cravings
- Balanced appetite
- Overall metabolic wellness
Key Ingredients You May Want to Highlight
- Cinnamon extract
- Berberine
- Chromium
- Bitter melon
- Alpha-lipoic acid
- Fenugreek
Each ingredient is chosen for its role in supporting a balanced internal environment.
Who May Benefit?
People looking to support:
- Healthy energy levels
- Appetite control
- Wellness routines
- Metabolic balance
How to Use
Take as directed on the label and follow with consistent healthy habits. Supplements work best as part of a larger wellness strategy.
One-Day Blood Sugar-Friendly Meal Plan
Here is a simple sample plan:
Breakfast
- Scrambled eggs with spinach
- Oatmeal with chia seeds
- Berries on the side
Lunch
- Grilled chicken or tofu
- Quinoa or brown rice
- Steamed vegetables
Dinner
- Baked salmon
- Roasted broccoli
- Sweet potato (small portion)
Snacks
- Nuts
- Greek yogurt
- Apple slices with nut butter
These meals focus on fiber, protein, healthy fats, and slow-digesting carbs.
Common Mistakes When Managing Blood Sugar
1. Skipping Meals
This often leads to crashes followed by overeating.
2. Eating Too Many “Healthy” Carbs
Granola, smoothies, and fruit juices can have more sugar than expected.
3. Relying on Supplements Alone
They are helpful, but lifestyle choices matter most.
4. Ignoring Sleep & Stress
Both have a direct impact on glucose regulation.
When to Talk to a Healthcare Professional
If you experience:
- Persistent fatigue
- Blurry vision
- Extreme thirst or hunger
- Very fast glucose changes
…it’s important to consult a doctor. Professional guidance ensures safe, individualized support.
Faqs
1. Does milk raise blood sugar?
Yes, milk can raise blood sugar because it contains lactose, a natural sugar. However, it usually causes a moderate increase, not a sharp spike, because milk also contains protein and fat, which slow digestion. Unsweetened dairy or alternatives (like almond milk) generally have a lower impact.
2. What is blood sugar?
Blood sugar (or blood glucose) is the amount of sugar circulating in your bloodstream. Your body uses it for energy, and levels naturally rise and fall throughout the day.
3. What is a normal blood sugar range?
Typical healthy ranges are:
- Fasting: 70–99 mg/dL
- Before meals: 70–130 mg/dL
- 1–2 hours after meals: Under 140 mg/dL
4. What causes blood sugar spikes?
Common triggers include sugary foods, refined carbs, stress, dehydration, poor sleep, and long periods of inactivity.
5. What are signs of high blood sugar?
Symptoms may include increased thirst, fatigue after meals, frequent urination, headaches, blurry vision, and increased appetite.
6. How can I lower blood sugar naturally?
Walking after meals, eating low-glycemic foods, staying hydrated, prioritizing sleep, reducing stress, and adding fiber-rich foods can help support steadier levels.
7. How often should I check my blood sugar?
This varies by individual. Some people check daily, while others monitor weekly or only during certain times. Always follow guidance from a healthcare provider.
8. Do artificial sweeteners affect blood sugar?
Most sugar-free sweeteners don’t significantly raise blood sugar, but responses vary by person, and some may impact appetite or digestion.
9. Can stress raise blood sugar?
Yes. Stress increases cortisol, a hormone that signals the liver to release glucose into the bloodstream, causing higher levels.
10. Can supplements support healthy blood sugar levels?
Some supplements contain herbs, minerals, or antioxidants traditionally used for metabolic support. They may complement diet and lifestyle, but they are not a replacement for medical advice or treatment.
Conclusion: Your Path to Balanced Blood Sugar
Healthy blood sugar isn’t just about numbers on a chart. It’s about how you feel every day—your energy, mood, focus, and long-term wellness.
By understanding how glucose works and adopting simple daily habits, you can naturally support more stable levels. And if you’d like additional help, adding a well-formulated supplement—such as Sugarmute—can be a valuable part of your daily routine.
Better balance starts with small, consistent steps. Your body will thank you.

